Introduction
Digital payment is a modern method of financial transactions that eliminates the need for cash by allowing individuals and businesses to transfer money electronically. With rapid technological advancements, digital payment systems have gained widespread adoption due to their convenience, speed, and security. This essay explores digital payments, how they work, their security mechanisms, potential threats, and their impact on global commerce.
1. What is Digital Payment?
Digital payment refers to the process of transferring money electronically using digital platforms, eliminating the need for physical cash or checks. Transactions are processed via online banking, mobile wallets, payment gateways, and other digital financial services. Governments and businesses worldwide are promoting digital payments to enhance financial inclusion and efficiency.
1.1 Types of Digital Payments
- Bank Transfers (NEFT, RTGS, IMPS) – Electronic fund transfers between bank accounts.
- Credit/Debit Cards – Widely used for online and offline transactions.
- Mobile Wallets (Paytm, Google Pay, Apple Pay) – Apps storing money digitally for easy payments.
- UPI (Unified Payments Interface) – Instant bank-to-bank transfers using mobile applications.
- QR Code Payments – Quick transactions by scanning a merchant’s QR code.
- Cryptocurrency Payments – Decentralized digital currency transactions.
- NFC (Near Field Communication) Payments – Contactless payments using tap technology.
2. How Digital Payment Works
Digital payments rely on electronic communication between banks, merchants, and customers through secure networks. The general process involves:
2.1 Transaction Initiation
- The payer selects a digital payment method (card, UPI, mobile wallet, etc.).
- Payment details are entered, or contactless authentication is used.
2.2 Authorization & Processing
- The payment request is sent to the payment processor.
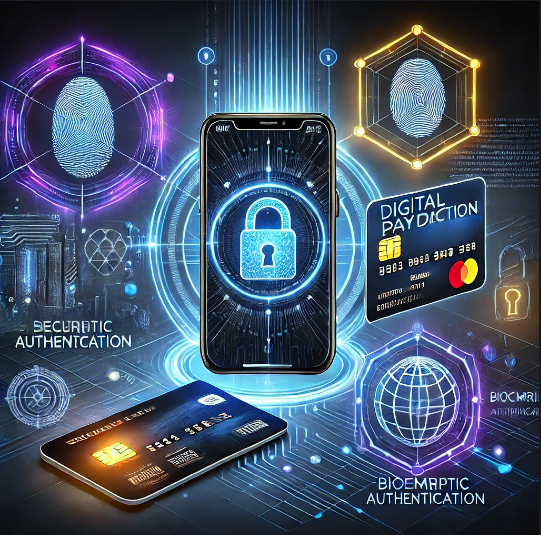
- Banks verify the transaction and authenticate using security measures like OTP or biometric authentication.
- Once verified, the amount is debited from the payer’s account and credited to the payee’s account.
2.3 Settlement & Confirmation
- A confirmation message is sent to both parties.
- Banks finalize settlements at the backend.
- The transaction is recorded in financial statements for future reference.
3. Security in Digital Payments
As digital transactions involve financial data, robust security measures are implemented to prevent fraud and unauthorized access.
3.1 Encryption & Tokenization
- Encryption: Converts transaction data into unreadable code to prevent hacking.
- Tokenization: Replaces sensitive data with unique symbols, ensuring security.
3.2 Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
- Users must verify transactions via OTP, biometrics, or PINs.
3.3 Secure Payment Gateways
- Payment gateways like PayPal and Razorpay provide additional layers of protection.
3.4 Fraud Detection & AI Monitoring
- AI-powered systems monitor suspicious activities and detect fraud in real time.
4. Threats in Digital Payments
Despite advanced security measures, digital payments are vulnerable to several threats:
4.1 Phishing & Identity Theft
- Fraudsters trick users into revealing personal information via fake websites or emails.
4.2 Malware & Ransomware Attacks
- Malicious software can steal payment details or lock access to financial data.
4.3 Card Skimming
- Criminals use unauthorized devices to capture card information at ATMs or POS terminals.
4.4 Account Takeover Fraud
- Hackers gain control of user accounts through weak passwords or leaked credentials.
4.5 Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
- Cybercriminals intercept communication between users and banks to alter transaction details.
5. Benefits of Digital Payments
Digital payments have revolutionized global financial systems, offering multiple advantages:
5.1 Convenience & Speed
- Transactions are processed instantly, reducing dependency on physical banking.
5.2 Financial Inclusion
- Digital payments enable underbanked populations to access financial services.
5.3 Reduced Fraud & Theft
- Electronic transactions reduce risks associated with cash handling.
5.4 Government Transparency & Revenue Growth
- Digital payments help curb corruption and improve tax collection.
6. The Future of Digital Payments
The future of digital payments is driven by emerging technologies and innovations:
6.1 Blockchain & Cryptocurrency
- Decentralized finance (DeFi) is reshaping the financial landscape with secure, transparent transactions.
6.2 Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning
- AI-powered chatbots, fraud detection, and predictive analytics are enhancing digital payment experiences.
6.3 Biometric Payment Systems
- Fingerprint and facial recognition will provide seamless and secure transactions.
6.4 Contactless Payments Expansion
- NFC and QR code-based payments are set to dominate the market.
Conclusion
Digital payment systems are transforming the financial world by making transactions more efficient, secure, and accessible. While challenges like cybersecurity threats persist, continuous advancements in encryption, AI-driven security, and decentralized finance will further strengthen digital payment ecosystems. As governments and businesses continue promoting digital transactions, the future of cashless economies appears promising, offering unparalleled convenience and financial growth opportunities.